Migraine is a prevalent and debilitating neurological disorder. It is characterised by unilateral, throbbing, or pulsating pain that can range from moderate to severe.
Depending on the frequency of the headaches, migraines can be considered episodic (less than 15 headache days a month) or chronic (15 or more headaches days a month).
June is National Migraine and Headache Awareness Month and plays a vital role in raising public awareness, knowledge, and advocacy.
Migraines are a health concern because they lead to reduced productivity and work efficiency.
After all, patients experience severe pain, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound during episodes.
Women are also three times more likely to experience migraines than men.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
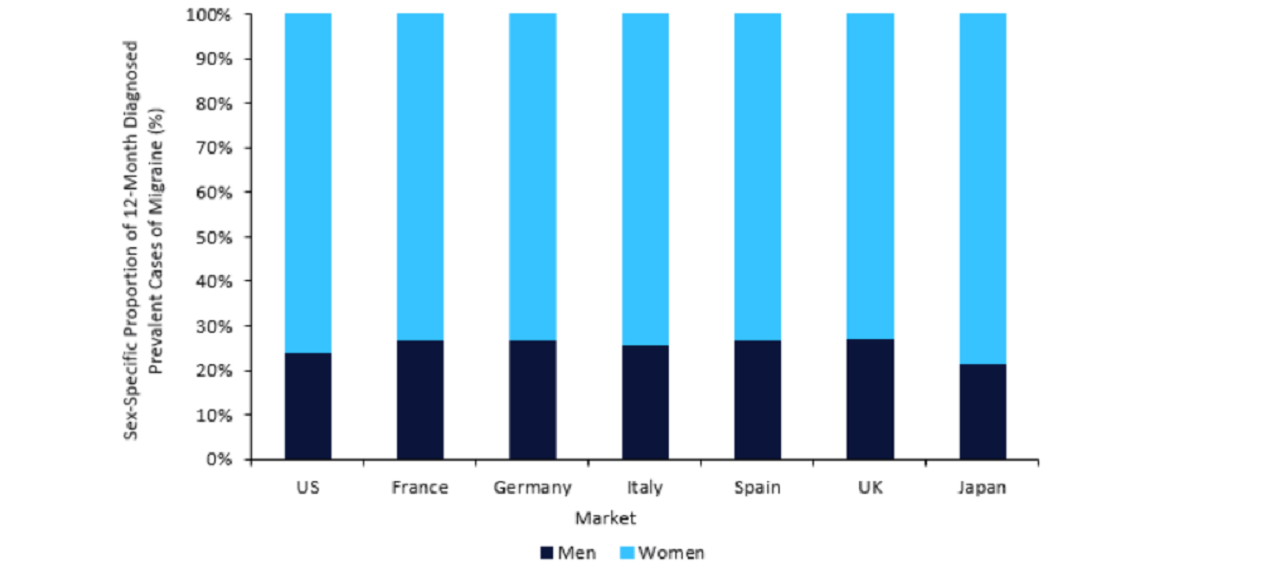
By GlobalDataAccording to leading data and analytics company GlobalData’s forecast, in the seven major markets (7MM: US, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, UK, and Japan), migraines are more common in women than men in 2024 (Figure 1).
More than 70% of the 12-month diagnosed prevalent cases in each of the 7MM presented in women in 2024.
The diagnosed prevalent cases in women in the combined 7MM were approximately three times higher than those of men.
Insights from the ‘Global Burden of Disease Study 2021’ highlight other notable gender differences such as women are more likely to experience longer headaches, migraine symptoms, and disability due to migraines.
These gender differences suggest that hormones influence the onset of migraine headaches.
According to the American Migraine Foundation, a decrease in estrogen can cause more frequent and intense migraine attacks.
As women go through different stages of life, these estrogen fluctuations may impact their treatment options.
Considering gender differences in disease presentation is important because migraine attacks manifest in different ways in men and women, requiring attention to events such as menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause when addressing treatment and migraine triggers.
For example, women may have unique considerations related to hormone replacement therapy (HRT) during menopause since some HRT regimens may exacerbate migraine symptoms while others can lead to an improvement.
By comprehensively addressing gender differences, physicians can enhance disease management, improve patient outcomes, and advance efforts to reduce the economic and physical burden of the disorder.