Artesunate for Injection is an antimalarial drug indicated for the initial treatment of severe malaria in adult and paediatric patients. It is the only drug in the US to treat the condition.
The complete treatment course of patients with severe malaria comprises intravenous (IV) artesunate followed by an appropriate oral antimalarial regimen.
Artesunate for Injection has been included in the World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines, as well as in ‘artemisinin derivatives’ group of drugs.
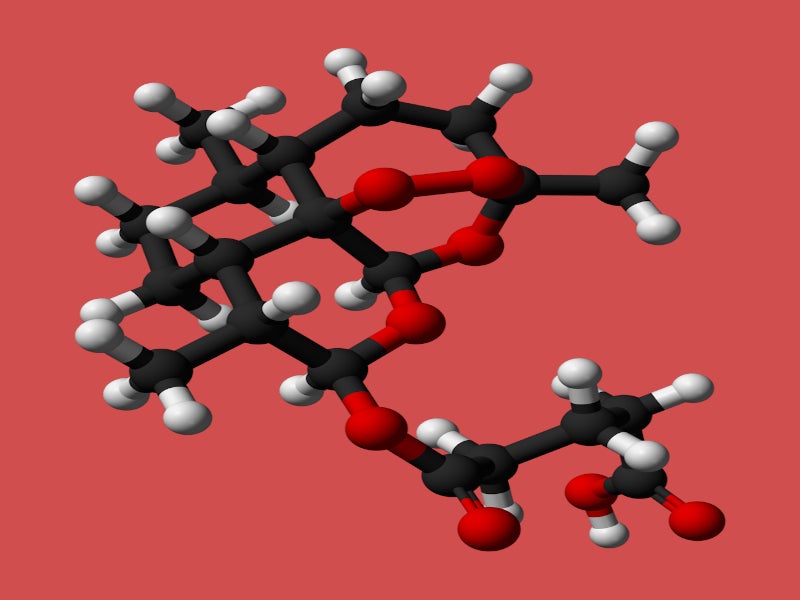
Artesunate for Injection is available in a single-dose vial containing 110mg of artesunate in white, sterile, fine crystalline powder form for constitution with the supplied sterile diluent for intravenous injection.
Artesunate for Injection approval
An investigational new drug (IND) application for artesunate was submitted by the US Army Office of the Surgeon General (OTSG) in 2004.
Development of the drug has been controlled by US Army Medical Research and Development Command (USAMRDC). The Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR) and the US Army Medical Materiel Development Activity (USAMMDA) collaborated under the USAMRDC for the constant supply of IV artesunate to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), since 2007.
WRAIR / USAMMDA partnered with an Italian company Sigma-Tau Industrie Farmaceutiche Riunte to develop a new drug application (NDA) for the IND IV Artesunate to treat severe and complicated malaria, in July 2019.
USAMMDA collaborated with Amivas for the modernised manufacturing and registration of the product with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), under a research and development agreement.
The NDA received priority review status and Artesunate for Injection was approved in May 2020.
The drug was earlier available to patients only through the FDA’s Expanded Access programme of CDC. FDA approval of the Artesunate for Injection will improve the accessibility of the life-saving drug to patients.
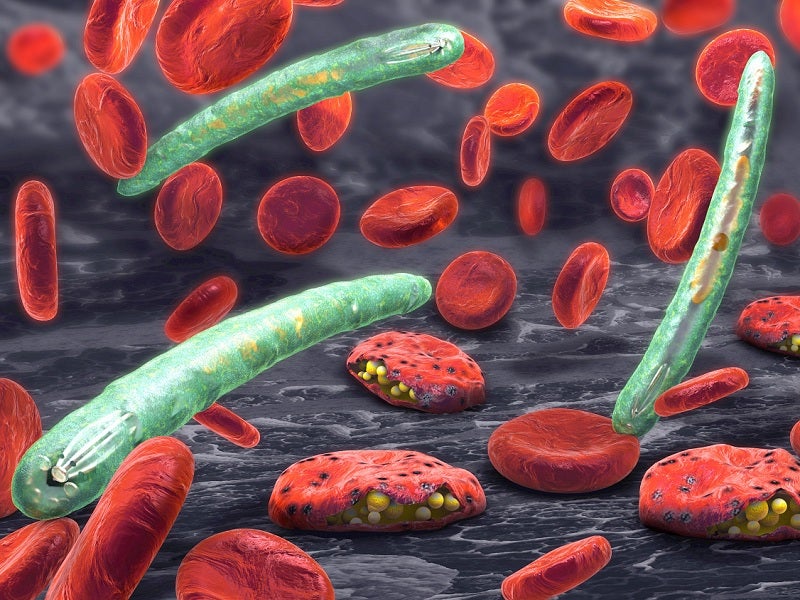
Malaria causes and symptoms
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease caused by the plasmodium parasite. Approximately 2,000 people are diagnosed with malaria every year in the US, of which 300 people suffer from severe malaria.
The most common symptoms of the disease are fever, chills and other flu-like symptoms. It may lead to other severe complications such as seizures, kidney failure, hallucination, coma or death, if not treated properly.
Artesunate mechanism of action
Artesunate is quickly metabolised into dihydroartemisinin (DHA), an active metabolite. Both block various asexual forms of the Plasmodium parasites, clearing the parasites in the blood within 48 to 72 hours.
Clinical studies on Artesunate for Injection
The FDA’s approval of the drug was based on a randomised, multi-centre, open-label controlled clinical study (Trial 1) in Asia, supported by another randomised, multi-centre, open-label controlled study (Trial 2) in Africa. The safety and efficacy of the drug were evaluated in clinical studies.
In Trial 1, 1,461 severe malaria patients, including 202 paediatric patients, were randomised to receive either IV artesunate or quinine, a comparator drug. The in-hospital mortality rate was found to be 13% in the artesunate group, which was much lower compared to 21% in the quinine group.
In Trial 2, 5,425 paediatric patients with severe malaria were treated with either artesunate or quinine. The trial also exhibited a significantly lower number of deaths in the artesunate group compared to quinine group.
The safety profile was found to be similar in both the clinical trials.
Common adverse events reported in patients treated with Artesunate for Injection during clinical trials were acute renal failure requiring dialysis, haemoglobinuria and jaundice.