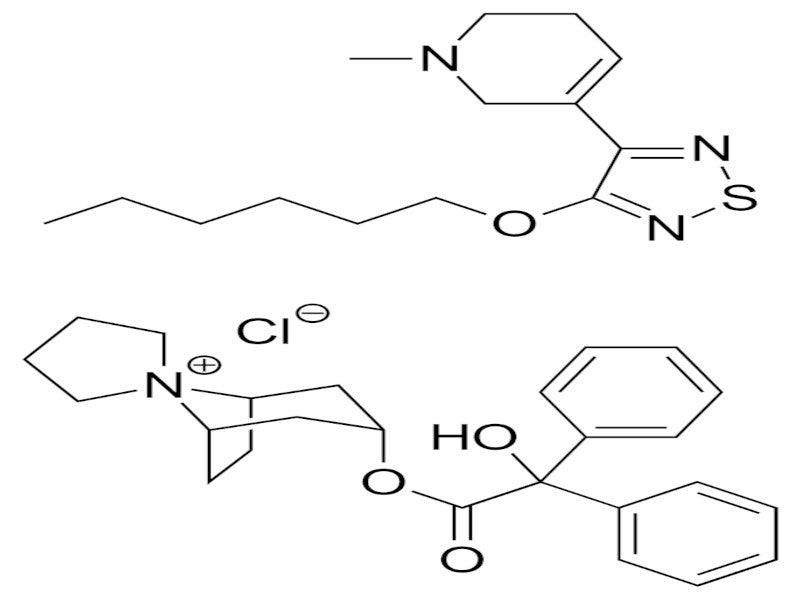
COBENFY™ (xanomeline and trospium chloride) is an antipsychotic drug combining xanomeline, a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) agonist, and trospium chloride, a muscarinic antagonist. The drug is indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults.
COBENFY, previously known as KarXT, was originally developed by Karuna Therapeutics, a biopharmaceutical company based in the US.
Zai Lab, a biopharmaceutical company based in China, obtained exclusive rights to develop, manufacture, and commercialise KarXT in Greater China and its surrounding areas, including mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan, in November 2021.
In March 2024, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), a pharmaceutical company based in the US, acquired Karuna Therapeutics and added KarXT to its product portfolio.
COBENFY is available as an oral capsule with dosage strengths of 50mg/20mg, 100mg/20mg and 125mg/30mg xanomeline/trospium chloride. The 50mg/20mg capsule is buff coloured while the 100mg/20mg and 125mg/30mg capsules are brown and Swedish orange, respectively.
Regulatory approvals for COBENFY
COBENFY was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in September 2024, making it the first therapy with a novel mechanism of action to be approved for schizophrenia in several decades.
Karuna Therapeutics’ New Drug Application (NDA) for KarXT was accepted by the FDA in November 2023, following the company’s submission of the NDA in September 2023.
Schizophrenia causes and symptoms
Schizophrenia is a chronic and debilitating mental disorder that impacts the way an individual thinks, feels, and acts. The primary causes triggering the disease could be genetic factors, psychosocial stressors, and environmental influences.
Symptoms typically manifest in early adulthood and vary from person to person. Schizophrenia is characterised by a range of symptoms, including positive and negative ones, as well as cognitive deficits.
Symptoms are hallucinations, delusions, and disorganised thinking or behaviour, as well as reduced physiological functions, diminished motivation, and social withdrawal.
Cognitive deficits include changes to memory, learning capabilities, and attention. Schizophrenia ranks among the top 15 leading causes of disability across the world. It affects approximately 24 million individuals globally, with 2.8 million cases reported in the US alone.
COBENFY’s mechanism of action
COBENFY is a first-in-class M1 / M4 muscarinic receptor agonist. The limbic and cortical areas of the central nervous system (CNS) possess M1 and M4 receptors, along with dopaminergic receptors.
These receptors are crucial in the regulation of cognition and play a significant role in the control of psychotic and behavioural disturbances, as well as in the improvement of negative and/or cognitive symptoms.
Xanomeline primarily targets the M1 and M4 receptors in the brain without blocking dopamine D2 receptors. It binds to them with similar affinity and shows marked agonist activity. In contrast, trospium chloride primarily acts as a muscarinic receptor antagonist in the peripheral tissues without crossing the blood-brain barrier.
Trospium chloride also reduces the adverse effects associated with xanomeline.
The exact mechanism of action of COBENFY is not yet fully understood.
Clinical trials on COBENFY
The FDA approval of COBENFY was supported by the data from the EMERGENT clinical programme.
The programme includes two Phase III clinical trials, EMERGENT-2 and EMERGENT-3, which are randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, focussing on the efficacy and safety of the drug.
Additionally, the programme includes two 52-week open-label studies, EMERGENT-4 and EMERGENT-5, designed to evaluate the long-term safety and tolerability of COBENFY for a duration of up to one year.
The EMERGENT-2 trial was a flexible-dose, five-week, inpatient study, whereas EMERGENT-3 was a multicentre, five-week trial.
The primary endpoint for both trials was the change in schizophrenia symptoms compared to placebo as measured by the positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) total score change from baseline to week five.
In both EMERGENT-2 and EMERGENT-3, COBENFY achieved its primary endpoint, with a 9.6-point and an 8.4-point reduction in the PANSS score compared to placebo at week five, respectively.
The results indicate a significant reduction in schizophrenia symptoms when compared to the placebo.
The most common adverse events reported in the patients were nausea, dyspepsia, constipation, vomiting, hypertension, abdominal discomfort, diarrhoea, tachycardia, dizziness, and gastroesophageal disorders.