According to GlobalData’s Clinical Trials Database, clinical trials of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T therapies peaked in 2021 with 272 taking place. There have been 217 clinical trials of CAR-T therapies up to July 2024, and GlobalData expects the year’s total number of trials to exceed those in 2021.
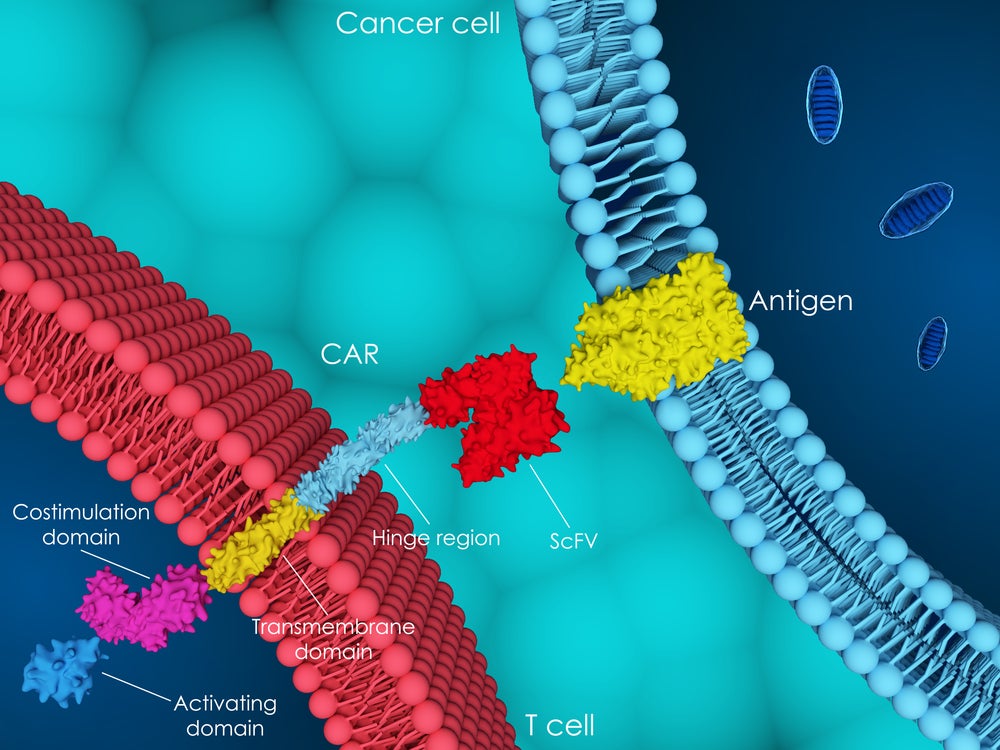
CAR-T therapy is a type of immunotherapy that involves modifying a patient’s T-cells to target and destroy cancer cells. This treatment has shown success in treating blood cancers such as leukaemia and lymphoma. T-cells are genetically altered in a lab to produce a receptor that targets specific proteins in cancer cells. Once reintroduced into the patient’s bloodstream, these modified cells seek out, attack and destroy cancer cells.
US Food and Drug Administration-approved CAR-T therapies, such as Novartis’s Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel), Kite Pharma’s Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel), and Kite Pharma’s Tecartus (brexucabtagene autoleucel), have been developed for various types of cancer. While these therapies have shown promise in clinical trials, they can also have significant side effects, requiring careful monitoring of patients.
Insurers and government programmes may be reluctant to cover costly treatments
In August 2017, Kymriah broke ground by becoming the first CAR T-cell therapy in the world to gain approval to treat acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in the US, followed closely by Yescarta. Both therapies were approved in Europe the following year. The fact that these treatments were initially approved in the US shows how CAR-T development was centered primarily in the West, more specifically the US, in the mid-2010s. Between 2010 and 2014, more than half of newly identified CAR-T therapies were being developed or co-developed by a US-based company. Key major players in this field are Novartis, Gilead, and Bristol Myers Squibb. Bristol Myers Squibb is one of the leading patent filers in the CAR T-cell therapy market.
Obstacles within the CAR-T market are mainly financial. CAR-T therapy is an expensive form of cancer treatment, with costs ranging from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars per patient. This can create financial barriers for patients who are unable to afford the treatment, as well as for healthcare providers and insurers who may struggle to cover their costs.
Due to the high cost of CAR-T therapy, insurers and government programmes may be reluctant to cover the treatment. This can create challenges for patients and healthcare providers who are trying to access and administer the therapy. In addition to the cost of the therapy itself, there are also significant manufacturing costs associated with CAR-T therapy. These include the cost of developing and scaling up the manufacturing process, and of the specialised equipment and facilities needed to produce the therapy.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData