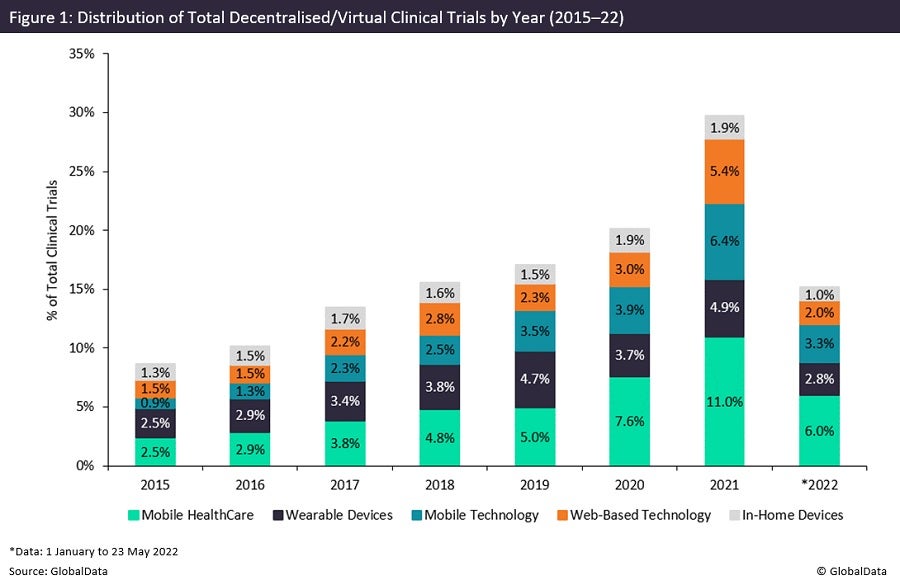
Covid-19 has proven highly disruptive to the pharmaceutical industry and necessitated innovation at record speeds to manage the harmful effects of the pandemic. Figure 1 highlights a growing trend in the number of decentralised/virtual trial initiations, with consecutive year-on-year growth since 2015. It is evident that the pandemic has strongly expedited the development of decentralisation in clinical trials, with last year showing a record 50% increase in decentralised and virtual trial initiations from 2020. Increased utilisation of these techniques would allow sponsors to adapt to the disruptive effects of the pandemic.
From 2015 to 2019, studies involving either mobile healthcare or wearable device components are closely matched. During the pandemic, however, we see a significant increase in the number of trials involving mobile healthcare, more than doubling in usage from 2019 to 2021. Owing to site closures and redeployment of sites for Covid-19 treatment and research, we observe an increasing requirement for mobile healthcare as a means of maintaining the integrity of clinical trials.
The overwhelming majority of studies that adopt mobile healthcare utilise telemedicine, with the use of this component on track for a record year in 2022. Interestingly, though the burden of Covid-19 on clinics and hospitals is decreasing, the use of telemedicine is still significantly increasing. This suggests the increased use of telemedicine is not a temporary trend, with the technology showcasing the evolution of clinical trials, with more accessible research and increasing diversity in studies.
The pandemic, however, resulted in wearable research being the only decentralised or virtual component, with decreased use in clinical trials initiated in 2020. This may be due to supply chain issues or difficulty incorporating wearable components when the subject activity or normal functions in general have been altered by lockdown restrictions. Last year, wearables research showcased a more robust performance, with a record number of trial initiations, and further growth is projected into this year.
The use of mobile technology in clinical trials has shown an increasing trend since 2015, with the greatest increase in trial initiations observed between 2020 and 2021. This suggests that many sponsors did not have the required infrastructure to immediately begin incorporating mobile technology into clinical trials when the pandemic first occurred. Despite this, last year saw sponsors implement increased use of mobile technology, suggesting heavy investment in the infrastructure that is required for implementation during this period.
The use of web-based technology in clinical trials has also shown an increasing trend since 2015, but based on available data, the use of such technology is scheduled to fall from record use last year. This is partly due to an increase in face-to-face consultations with the lifting of Covid-19 restrictions, as well as patient reluctance in using some of these components owing to their complexity of use.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData