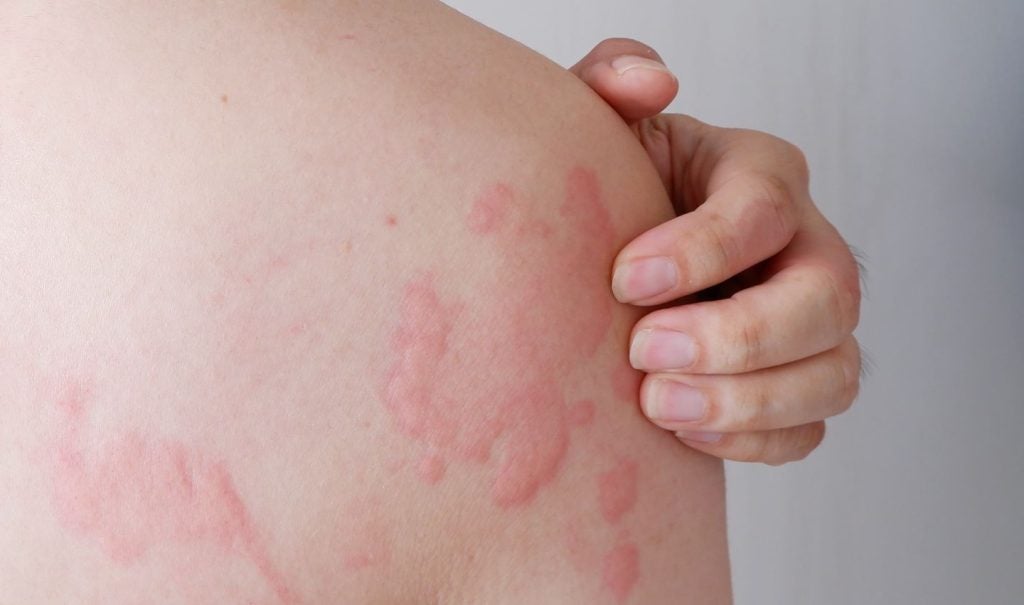
Evommune has commenced a Phase I first-in-human clinical trial of new oral treatment, EVO756, for chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU).
The trial will assess the tolerability, safety and pharmacokinetics of EVO756 in healthy adult participants and adult CSU patients.
This randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind study will analyse single and multiple ascending doses (SAD and MAD) in healthy adults, alongside an open-label study in CSU patients.
A key aspect of the trial is the pharmacodynamic assessment of EVO756's impact on mast cell degranulation. This will be evaluated through a skin challenge test, where a known ligand of the X2 receptor is administered intradermally to induce measurable skin responses.
A small molecule antagonist of the mas-related G-protein coupled receptor X2 (MRGPRX2), EVO756 has shown to be a robust oral treatment option for various mast cell-mediated ailments by hindering the activation of MRGPRX2 and mast cell degranulation in pre-clinical research.
Additionally, EVO756's action on peripheral sensory neurons may offer rapid relief from itch linked to inflammatory ailments, such as atopic dermatitis.
EVO756 could become a potential once-daily oral treatment for such ailments and could avoid the serious side effects associated with other treatments.
Evommune chief medical officer Eugene Bauer said: “As a company committed to developing a pipeline of therapeutics to halt the progression of chronic inflammatory diseases, we are excited to dose the first volunteer in our Phase I trial of EVO756.
“By targeting mast cells via the selective modulation of MRGPRX2, we aim to deliver a novel therapeutic with the efficacy of a biologic and the potential for once-daily oral administration, without the safety challenges of alternative mast cell depleting options.
“In CSU patients, blockade of the MRGPRX2 receptor and its subsequent downstream effect has the potential to treat the root cause of inflammation, offering greater relief than currently available treatments.”