Doptelet® (avatrombopag) is one of the first thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonists to be approved in the US for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in adult patients with chronic liver disease (CLD).
Discovered and developed by Dova Pharmaceuticals, Doptelet’s new drug application (NDA) was accepted and granted priority review by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in November 2017. The FDA then approved the drug in May 2018.
Dova Pharmaceuticals also submitted a marketing authorisation application (MAA) for Doptelet to the European Medicines Agency (EMA), which approved the same in June 2019.
In September 2018, Dova Pharmaceuticals submitted a supplemental NDA (sNDA) for Doptelet to the FDA for the treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP) in adult patients.
The FDA accepted the sNDA for review in November of that year and approved the same in June 2019 expanding the use of Doptelet in ITP patients who have had an insufficient response to a previous treatment.
Dova is also investigating Doptelet for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia (CIT) and thrombocytopenia in patients undergoing invasive surgical procedures.
Thrombocytopenia in chronic liver disease
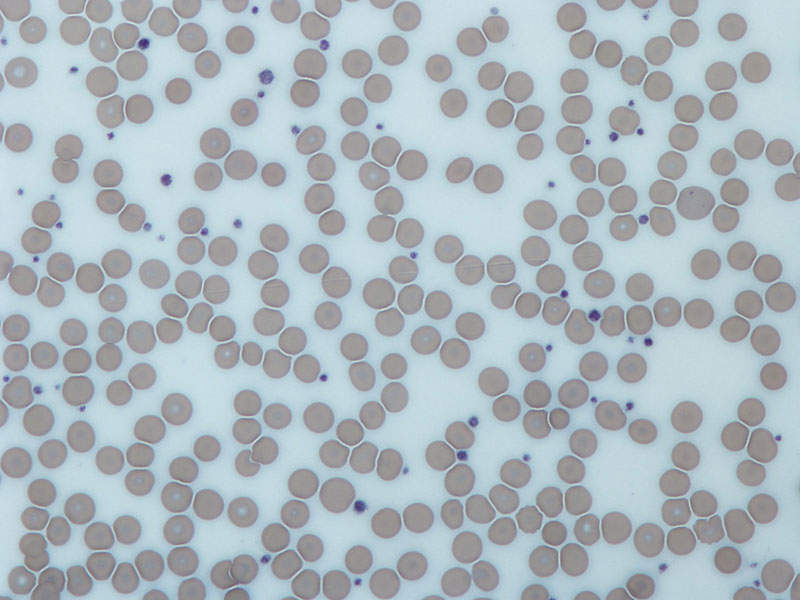
Thrombocytopenia is characterised by the reduction of the number of platelets in the blood. The disease is a common complication in patients with CLD and it occurs due to a reduction in TPO, a physiologic regulator of platelet production.
TPO production decreases in CLD patients with liver damage and results in thrombocytopenia.
The symptoms of the disease include easy or excessive bruising, prolonged bleeding from cuts, bleeding from the gums or nose, blood in urine or stools, heavy menstrual flows, fatigue, enlarged spleen and jaundice.
According to the National Cancer Institute (NCI), approximately 70,000 patients with CLD have a platelet count of less than 50,000 / µl.
Doptelet’s mechanism of action
Doptelet contains a TPO receptor agonist, which stimulates proliferation and differentiation of megakaryocytes from bone marrow progenitor cells and results in increased production of platelets. It is designed to imitate the effects of TPO for normal platelet production.
The drug is available in 20mg dose tablets for oral administration.
Clinical trials on Doptelet
The FDA’s approval for Doptelet was based on results obtained from global Phase III clinical trials ADAPT-1 and ADAPT-2. These double-blind and placebo-controlled trials were conducted on 430 adults with thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic liver disease and platelet counts below 50,000 / µl.
The patients were randomised to receive either 40mg or 60mg of Doptelet daily for five days or placebo based on their baseline platelet counts.
Doptelet displayed superior efficacy in both the dosage groups when compared to placebo. The number of patients not requiring platelet transfusions or rescue procedures for bleeding up to seven days following a scheduled procedure was higher in the Doptelet group.
The results also showed that Doptelet was superior to placebo and met the secondary efficacy endpoints in both the trials.
The most common adverse reactions included pyrexia, abdominal pain, nausea, headache, fatigue and oedema peripheral.
The sNDA submission to the FDA for ITP treatment was supported by data from a randomised, placebo-controlled Phase III clinical study, which met its primary endpoint of a number of weeks with a platelet count of more than 50×109 / l without a rescue therapy.
Marketing commentary on Dova Pharmaceuticals
Headquartered in Durham, North Carolina, Dova Pharmaceuticals is involved in the acquisition, development and commercialisation of drug candidates for rare diseases.