Erivedge (vismodegib) is a Hedgehog pathway inhibitor indicated for the treatment of advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC) in adults. Roche and Genentech are developing the drug, in partnership with Curis. Erivedge was discovered by Genentech and tested in collaboration with Curis through several preclinical studies.
Roche submitted a new drug application (NDA) for Erivedge with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in September 2011. The FDA accepted the NDA and granted it priority review status in November 2011.
In January 2012, Erivedge became the first drug to be approved by the FDA for the treatment of advanced BCC. A marketing authorisation application (MAA) for Erivedge was submitted to the European Union (EU) in December 2011 and is currently being reviewed.
Advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
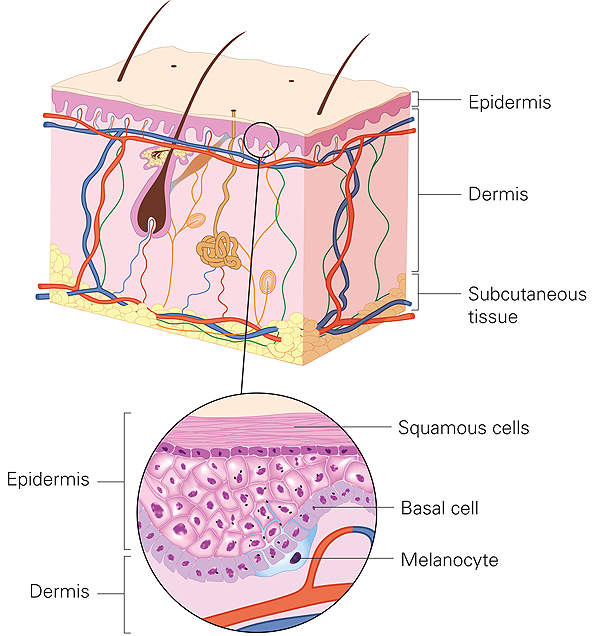
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of painless skin cancer, affecting nearly two million people across the world. It manifests on the top layer or epidermis of the skin upon regularly being exposed to sunlight or other ultraviolet radiation.
BCC is curable if it is constrained to a small region of the skin. Symptoms include the development of small lumps or lesions and eczema-like changes. These lesions can be removed through surgery as they advance slowly and usually do not metastasise.
In a small proportion of patients, BCC can spread deeper into the skin, causing severe disfigurement. In such cases, the disease can become life-threatening and is difficult to treat. Lesions or tumours formed in such cases are classified as advanced BCC and metastatic BCC.
Advanced BCC can affect other parts of the body such as bones and sensory organs such as eyes, the nose and ears. Metastatic BCC is much more severe, spreading to the lungs, liver, lymph nodes and bones. A person suffering from metastatic BCC has a median survival rate of eight months from diagnosis.
Erivedge – Hedgehog pathway inhibitor
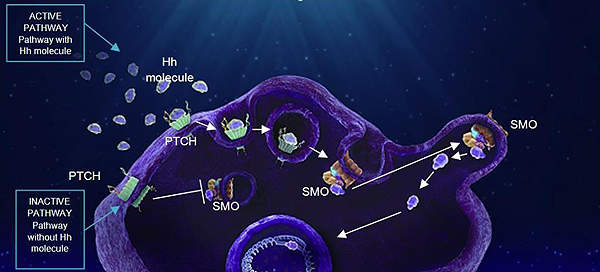
The Hedgehog signalling pathway plays a key role during the early stages of development and becomes inactive in adulthood.
Mutations in the pathway lead to reactivation of Hedgehog signalling and is known to cause several types of cancers.
Abnormal signalling in the pathway is known to be responsible for nearly 90% of BCC cases. Research has indicated that blocking of the Hedgehog pathway can be an effective treatment for BCC.
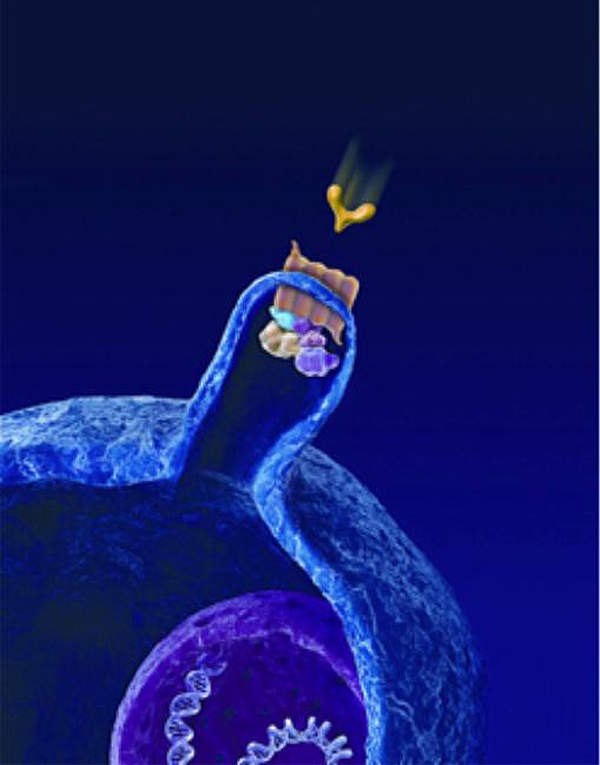
The Hedgehog pathway includes two key receptors on the cell surface – patched and smoothened. Mutations in either one of the receptors can lead to continuous cell growth and replication resulting in the formation of tumours.
Erivedge works by blocking irregular signalling in the pathway by attaching to the smoothened receptors.
Clinical trials of the skin cancer treatment drug vismodegib
Erivedge has been investigated in 12 Phase I clinical trials and two Phase Ib/II trials. A total of 14 Phase II clinical trials have been conducted.
Approval of Erivedge was based on the Phase II ERIVANCE BCC study which recruited 104 patients suffering from advanced BCC and metastatic BCC. The study was conducted across 31 centres in the US, Australia and Europe.
It started in September 2008 and was completed in October 2010. Results from the study indicated that Erivedge was effective in treating lesions in 43% patients with advanced BCC and 30% patients with metastatic BCC.
Marketing commentary for Roche and Genentech’s Erivedge
Erivedge is the first drug available for the treatment of advanced BCC and a good alternative for patients who cannot undergo surgery. This provides a prime position for the drug in the market with no competitors.
Genentech is responsible for marketing of Erivedge in the US and Chugai Pharmaceuticals in Japan. Roche is responsible for marketing the drug in the rest of the world.
Genentech awarded a $10m milestone payment to Curis following Erivedge’s approval. Curis will receive additional milestone payments if the MAA is approved. It is also entitled to royalties from future sales of Erivedge.