NOURIANZ (istradefylline) is indicated as adjunctive therapy to levodopa and carbidopa medications in adult patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) to treat “off” episodes, caused when existing medications are ineffective and lead to an increase in PD symptoms.
Developed by Kyowa Kirin, a pharmaceutical and biotechnology company based in Japan, the drug was approved by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) of Japan in 2013. It is being marketed under the brand name NOURIAST in Japan since May 2013.
Kyowa Kirin filed a new drug application (NDA) with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for NOURIANZ in April 2007 but received a not-approvable letter in February 2008. The company submitted a revised NDA for the drug in February 2019.
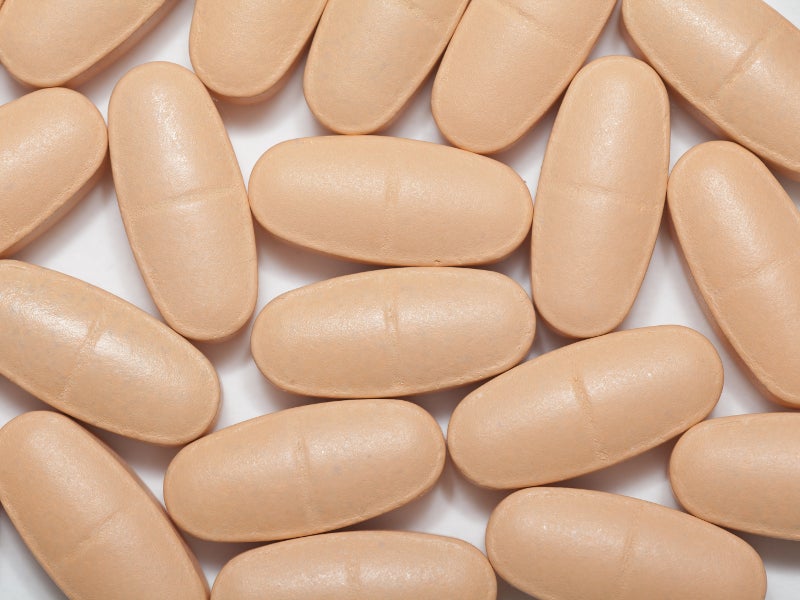
The FDA approved the drug in August 2019. NOURIANZ is available as once-daily peach-coloured, pillow-shaped film-coated tablets in 20mg and 40mg strengths.
Parkinson’s disease causes and symptoms
PD is a progressive, neurodegenerative disease characterised by motor symptoms such as shaking, stiffness, loss of balance and coordination, slowed movements, as well as posture instability and tremor.
The cause of PD is progressive degeneration associated with reduced dopamine levels in the substantia nigra and striatum of basal ganglia in the mid-brain. It occurs when brain cells or neurons that control the body movement become impaired or non-functional or die. The disease affects 50% more men than women. Most develop the disease at the age of 60, while 5-10% of individuals are diagnosed before the age of 50.
As the disease progresses, the patient may experience difficulty in walking and talking. Other symptoms of the disease include mental and behavioural symptoms, emotional changes, urinary and skin problems, insomnia, depression, memory loss and fatigue.
NOURIANZ’s mechanism of action
Istradefylline is a selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist used in addition to carbidopa and levodopa for the treatment of “off” episodes.
The precise mechanism of action of the drug is unknown but it is presumed to reduce the overactivity of the striatal pathway, restoring the balance of basal ganglia.
Clinical studies on NOURIANZ
FDA approval of NOURIANZ comes from the outcomes of four randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies conducted in PD patients experiencing “off” episodes.
The 12-week clinical studies enrolled a total of 1,143 participants suffering from PD for an average of nine years and experiencing at least two hours of “off” time a day. The primary endpoint of the studies was the percentage change from baseline in “off” time per day, while the change from baseline in “on” time without dyskinesia was the secondary endpoint.
Study 1 was conducted in the US and Canada, while Study 2 was conducted in the US. Patients were administered with NOURIANZ 20mg, 40mg or placebo. The percentage change from baseline was 16.2% for cases managed with NOURIANZ and 13.8% for those given placebo in Study 1, 14% for patients administered with NOURIANZ and 11.6% in the placebo group, in Study 2.
Studies 3 and 4, conducted in Japan, demonstrated a statistically significant decrease from baseline in “off” episodes in patients administered with NOURIANZ.
The most common adverse reactions reported during the trials were dyskinesia, hallucination, insomnia, constipation, dizziness and nausea.
Marketing commentary on Kyowa Kirin
Based in Japan, Kyowa Kirin is engaged in the development and marketing of prescription medicines.
Owned by Kirin holdings, Kyowa Kirin specialises in nephrology, oncology, central nervous system (CNS), immunology and allergy therapeutic areas.
Nesp, Regpara, Gran and Romiplat are some of the significant products marketed by the company.