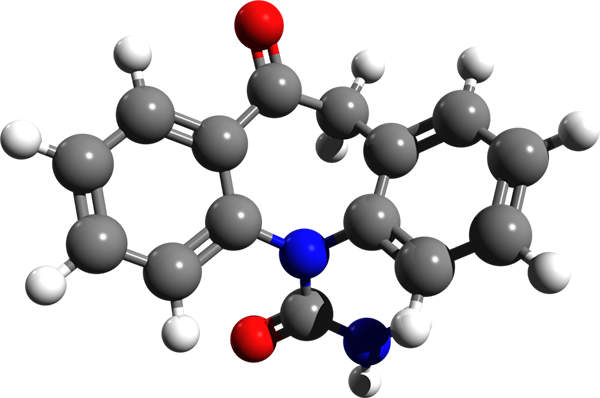
Oxtellar XR (oxcarbazepine/ SPN-804) is an anti-epileptic drug indicated for the treatment of partial seizures. The drug is developed, manufactured and marketed by Supernus Pharmaceuticals.
In October 2012, Supernus obtained approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for Oxtellar XR to treat adult patients and children aged between six and 17 years.
About partial seizures
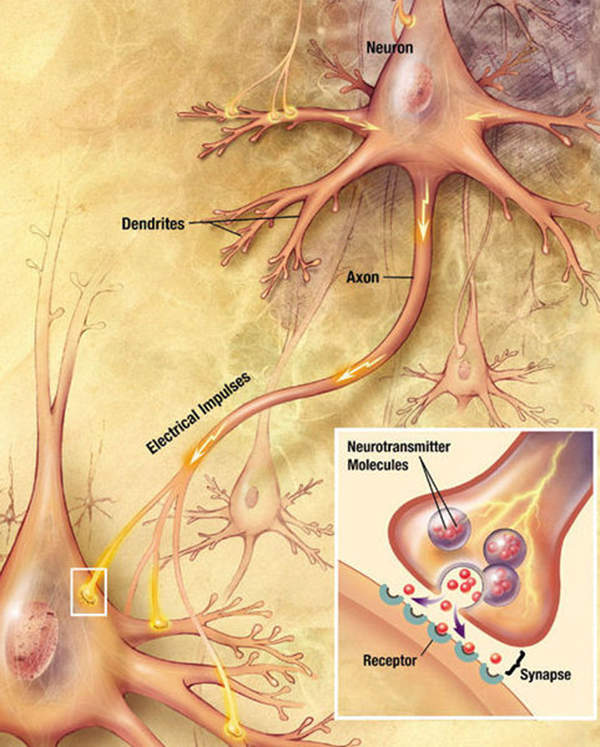
Partial seizures occur due to electrical disturbances to some part of the brain. The disease affects only part of the brain, because the electrical disturbance is limited to a specific area. The symptoms of the disease include loss of consciousness, sensory phenomena, transient weakness or loss of sensation, automatisms, and amnesia for seizure events.
It is estimated that seizures affect about three million people of all ages across the US. The disease is associated with about $17.6bn direct and indirect healthcare costs in the US.
Oxtellar XR’s mechanism of action
Oxtellar XR contains an anti-epileptic formulation known as oxcarbazepine. The drug stops the voltage-sensitive sodium channels and also inhibits the repetitive neuronal firing. The drug is available in tablet form for oral administration in 150mg, 300mg and 600mg doses.
Clinical trials on Oxtellar XR
Supernus Pharmaceuticals conducted Phase I clinical trials on Oxtellar XR between June 2009 and November 2010. It was an open-label, non-randomised, and pharmacokinetics study. The study was conducted on 40 patients with partial epilepsy. The primary outcome measure of the study was examining the pharmacokinetics (PK) and assessment of the safety and tolerability of Oxtellar XR.
The FDA Approval for Oxtellar XR for the treatment of partial seizures in children was based on a well controlled Phase III clinical trial conducted between June 2009 and June 2012. The primary outcome measure of the study was to evaluate the long-term administration of Oxtellar XR. The secondary outcome measures of the study included evaluation of the effect on seizure frequency of long-term administration of adjunctive Oxtellar XR. The study was conducted in 83 centres across the US.
The study enrolled more than 366 adults with refractory partial epilepsy. The subjects were administered with Oxtellar XR (1,200mg/day or 2,400mg/day) or placebo for initial phase of four weeks, which was followed by 12-week maintenance phase. The primary endpoint of the study was finding the median change from baseline in seizure frequency per 28 days.
The results of the study demonstrated that the patients treated with Oxtellar XR 1,200mg/day improved 38.2% in median change from baseline in seizure frequency, the patients administered with Oxtellar XR 2,400mg/day showed 42.9% change, and placebo-administered patients showed a change of 28.7%.
The study was further extended to 12 weeks in an adjunctive therapy trial. It was a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which the patients were administered with Oxtellar XR 600mg, 1,200mg and 2,400mg doses in a day, and placebo.
The results of the adjunctive therapy trial showed that the patients administered with all doses significantly improved in the reduction in seizure frequency when compared to placebo. The common side effects of the drug found during the clinical studies included dizziness, somnolence, headache, balance disorder, tremor, vomiting, diplopia, asthenia and fatigue. The post-marketing pharmacokinetic assessments on Oxtellar XR are expected to be submitted to the FDA in 2016.
Marketing Oxtellar XR in the US
Related project
Lamictal – Approved Treatment for Epilepsy and Bipolar, United States of America
Lamictal XR (lamotrigine), developed by GlaxoSmithKline, is an approved treatment for epilepsy and bipolar I disease. The drug was first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1994.
Supernus Pharmaceuticals holds the commercial rights for the Oxtellar XR in the US. The company launched Oxtellar XR in the US market in February 2013. Other anti-epileptic medications available in the market include Lamictal, developed by GlaxoSmithKline, and Trileptal, developed by Novartis.