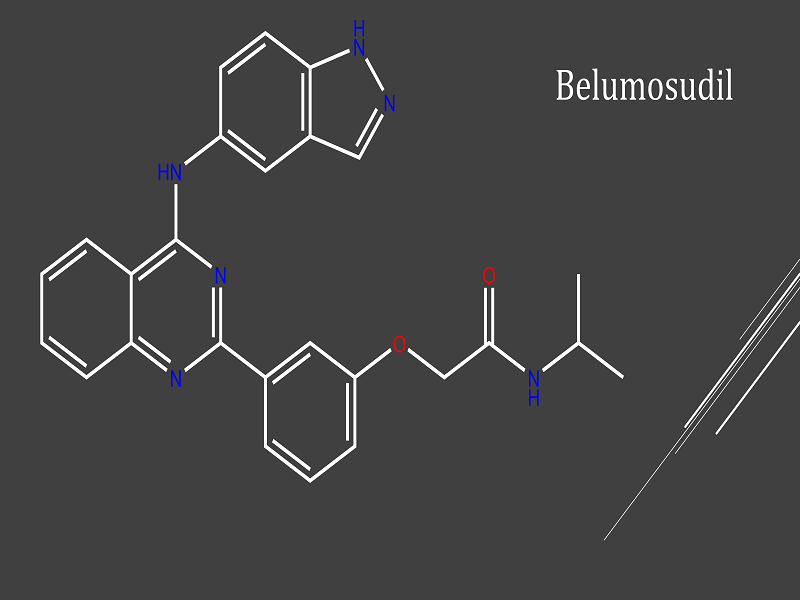
REZUROCK™ (belumosudil) is an oral kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) in patients aged 12 years and older who have received at least two failed previous lines of alternative systemic therapy.
Developed by US-based biopharmaceutical company Kadmon Holdings, REZUROCK is available as a pale-yellow film-coated oblong tablet of 200mg dosage strength. The company has selected Onco360®, an independent oncology pharmacy, as a speciality pharmacy partner for selling REZUROCK.
In December 2019, Kadmon collaborated with Japanese pharmaceutical company Meiji Seika Pharma, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Meiji Holdings, to exclusively develop and commercialise belumosudil in Japan and certain other Asian countries.
Regulatory approvals for REZUROCK
In October 2017, REZUROCK was awarded orphan drug designation by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of cGVHD.
In October 2018, the FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation (BTD) to belumosudil for the treatment of patients with cGVHD after the failure of two or more lines of systemic therapy.
Belumosudil secured orphan drug designation for the treatment of systemic sclerosis in September 2020. In the same month, Kadmon submitted a new drug application (NDA) to the FDA under the real-time oncology review (RTOR) pilot programme seeking approval of belumosudil for cGVHD.
The FDA accepted the NDA for priority review in November 2020 and approved the drug in July 2021.
Causes and symptoms of cGVHD
cGVHD is a condition that often develops within one year of an allogeneic stem cell transplant, leading to significant morbidity and mortality. The condition occurs when the transplanted immune cells (graft) attack the host’s (patient) cells, causing inflammation and fibrosis in multiple tissues.
The disease can affect multiple organ systems, including the oesophagus gastrointestinal tract, neuromuscular system, genitourinary tract, liver, lungs, mouth, eyes, muscles and joints. Around 14,000 people in the US currently live with cGVHD.
Symptoms of cGVHD include dry eyes, rashes with raised or discoloured areas, skin thickening, abdominal swelling, yellow discolouration of the skin and eyes, dry mouth, shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), fatigue, muscle weakness, and tightness in joints.
REZUROCK mechanism of action
REZUROCK is a small molecule inhibitor of Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase (ROCK), a signalling pathway that regulates the inflammatory response and fibrotic processes. It lowers proinflammatory responses by regulating the phosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT5 and modulating Th17/Treg balance in ex-vivo or in-vitro-human T cell assays.
Clinical trials on REZUROCK
The FDA’s approval of REZUROCK was based on the results of ROCKstar, a randomised, open-label, multi-centre Phase II clinical trial. The ROCKstar trial was conducted on cGVHD patients who had previously received between two and five lines of systemic therapy and required additional treatment.
In the study, 66 patients were administered with oral REZUROCK 200mg once a day. The study’s primary endpoint was the overall response rate (ORR) in patients.
In all but one of the 66 patients, the ORR was reported according to the 2014 NIH Response Criteria. This was achieved in 75% of patients, of who 6% showed complete response, while 69% achieved a partial response.
The median time to first response was 1.8 months and the median duration of response was 1.9 months. Around 62% of the patients did not require new systemic therapy for at least 12 months after achieving a response.
The drug was well-tolerated and adverse events were consistent with the advanced cGVHD patients who received corticosteroids and/or other immunosuppressants.
The most common adverse reactions reported in the patients treated with belumosudil in the clinical trial were laboratory abnormalities, infections, decreased muscle strength, nausea, diarrhoea, difficulty in breathing, cough, haemorrhage, and pain in the abdomen, muscles and skeleton.
Other reactions included headache, decrease in phosphate and lymphocytes, increase in gamma-glutamyl transferase, and hypertension.