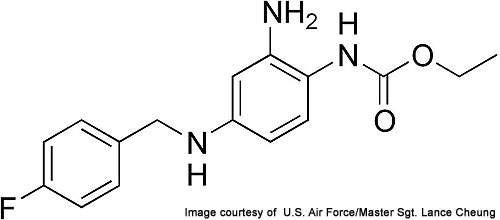
Trobalt (ezogabine / retigabine) is indicated for the treatment of partial-onset epileptic seizures in patients aged more than 18 years old. It is manufactured jointly by Canada-based Valeant Pharmaceuticals and GlaxoSmithKline.
GlaxoSmithKline submitted a marketing authorisation application for Trobalt to the European Medicines Agency in October 2009. It was approved in March 2011.
The drug has the non-propriety name ezogabine in the US and Canada, and retigabine in the rest of the world.
In October 2009, Valeant submitted a New Drug Application for ezogabine with the US Food and Drug Administration. The drug was approved by the US regulator in June 2011. It is manufactured under the trade name Potiga in the US and Canada. The drug was launched in the US in 2012.
In August 2011, the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence recommended Trobalt as an add-on treatment for patients with partial-onset seizures. The recommendation offers Trobalt as an option for physicians and patients to treat epilepsy.
Partial-onset epileptic seizure
Partial-onset seizure is a type of epilepsy, which occurs only in a specific part on one side of the brain. Epilepsy is a neurological disorder in which patients face seizures or convulsions at regular intervals of time.
Epileptic seizures, also known as fits, are a sign of an abnormal neuronal excitation in the brain. It may occur in patients with brain infections, trauma, dementia, stroke, AIDS, congenital brain defects, brain tumour or other diseases which damage the brain tissues.
Symptoms of partial onset seizures include gazing, lack of alertness and violent shaking prior to the seizure and some patients may smell a non-existent odour. Emotional changes may also be observed.
More than 50 million people worldwide suffer from epilepsy and partial onset seizures.
Mechanism of action of Trobalt (ezogabine / retigabine)
Neuronal activity in the brain is regulated by four ion or potassium channels, Na+, Cl+, Ca- and K+, otherwise designated as KCNQ channels. The excitability of the neurons is regulated by Na+ and Ca+ and the neuronal activity can be inhibited by Cl- and K+ ions.
Trobalt is a potassium channel agent, which activates the KCNQ channels and decreases the abnormal activity in the brain. Based on in-vitro studies, the augmentation of Gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA) (an inhibitory neurotransmitter) mediated currents is expected to enhance the therapeutic activity of the drug. GABA may play a vital role in suppressing the seizures.
Phase one and Phase two clinical trials
Pre-clinical trials were conducted in animals to determine the effect of the drug on the urinary tract. Urinary retention was observed in most of the animals.
More than 45 clinical trials have been conducted in around 2,247 patients, including 29 phase one and five phase two studies.
A phase one trial was conducted to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of five prototypes of the drug tablet formulation. The trial was initiated in February 2011 and recruited around 36 patients. The study was completed in June 2011.
Around 187 patients were enrolled for a phase two trial to compare the safety and efficacy of the drug with the placebo in epileptic seizure patients. The trial was initiated in October 2007 and completed in December 2009.
More than a quarter of the patients enrolled in phase one and two complained of urinary retention.
Approval of Trobalt was based on two phase three trials, namely Restore 1 and Restore 2.
Phase three trials of Trobalt (ezogabine / retigabine)
The Restore 1 trial was conducted to compare the safety and efficacy of the drug with that of a placebo. Initiated in September 2005, the trial enrolled around 280 patients and was completed by January 2008.
The Restore 2 trial enrolled around 539 patients. It was conducted to compare the safety and efficacy of 600mg and 900mg daily doses with that of a placebo. It was initiated in December 2005 and completed by April 2008.
In May 2006, a phase three trial was initiated to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug in patients suffering from partial onset epileptic seizures. The primary endpoint of the trial is to determine the change in frequency of seizures from the baseline. Around 181 patients have been enrolled for the study which was completed by 2012.
A phase three trial to determine the safety, tolerability and efficacy of the drug as a continuation therapy was initiated in July 2010. The trial enrolled around 235 patients who were administered 300mg or 1,200mg doses of the drug every day. The study was completed by 2012. The primary endpoint is to achieve more than 50% reduction in the 28-day partial onset seizures frequency.
Most of the patients enrolled in the clinical trials experienced adverse effects such as dizziness, somnolence, fatigue, vertigo, tremor, abnormal coordination, disturbance in attention, memory impairment, asthenia, gait disturbance, dysarthria and balance disorder. Patients being treated with Trobalt will require continuous monitoring to prevent urinary retention and kidney stones.
A phase three trial to evaluate the long-term safety, efficacy and tolerability of the drug in epileptic patients was initiated in February 2011.
Around 140 patients have been enrolled and were administered 300mg-1,200mg doses of the drug daily. The primary endpoint is to determine the rate of adverse events to that of the serious adverse events.
Marketing commentary
By 2017, the drug is expected to have annual sales of approximately $300m in seven countries, including the US, Japan and the UK.