VOQUEZNA™ is a novel first-in-class oral treatment containing vonoprazan, packaged with one or more antibiotics for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) infection in adults.
VOQUEZNA is developed by Phathom Pharmaceuticals, a biopharmaceutical company jointly launched by Takeda and Frazier Healthcare Partners for the development of new therapeutics, including Vonoprazan, for the treatment of acid-related disorders in North America and Europe in May 2019.
Phathom holds the license for the development and exclusive marketing of vonoprazan in the US, Europe and Canada, while Takeda owns the drug’s developmental and marketing rights in Japan and several other Asian markets.
VOQUEZNA is available in two treatment regimens, namely VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK™ (vonoprazan tablets, amoxicillin capsules, clarithromycin tablets) and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK™ (vonoprazan tablets, amoxicillin capsules).
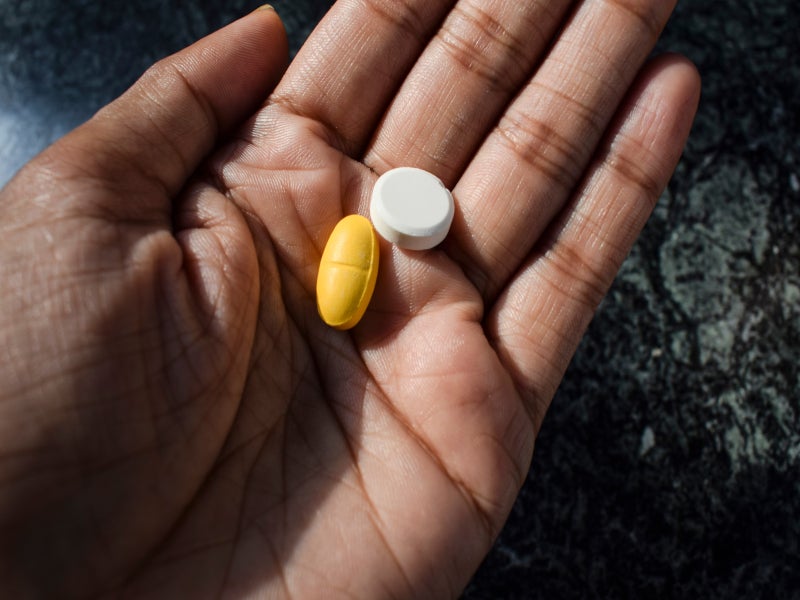
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK co-packages contain 14 administration packs each. Each VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK administration pack contains pale red, oval, film-coated 20mg vonoprazan tablets, yellow, opaque, hard gelatine 500mg amoxicillin capsules, and white, oval, film-coated 500mg clarithromycin tablets.
Each VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK administration pack contains 20mg of vonoprazan and 500mg of amoxicillin.
Regulatory approvals for VOQUEZNA
Vonoprazan was initially approved in Japan as vonoprazan fumarate under the brand name TAKECAB® for the treatment of acid-related diseases in December 2014. The drug has also been launched in several other Asian markets such as Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan, and Thailand.
In March 2020, Cabpirin® combination tablets containing vonoprazan fumarate and low-dose aspirin were approved in Japan, co-promoted by Takeda and Otsuka, to treat acid-related diseases.
In September 2021, Phathom submitted new drug applications (NDAs) for VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of H. pylori infection.
The FDA reviewed the products under priority review designation and approved them in May 2022. In the same month, the FDA accepted for review an NDA for vonoprazan for the treatment of erosive esophagitis (EE), which had been submitted by Phathom in March 2022.
VOQUEZNA’s mechanism of action
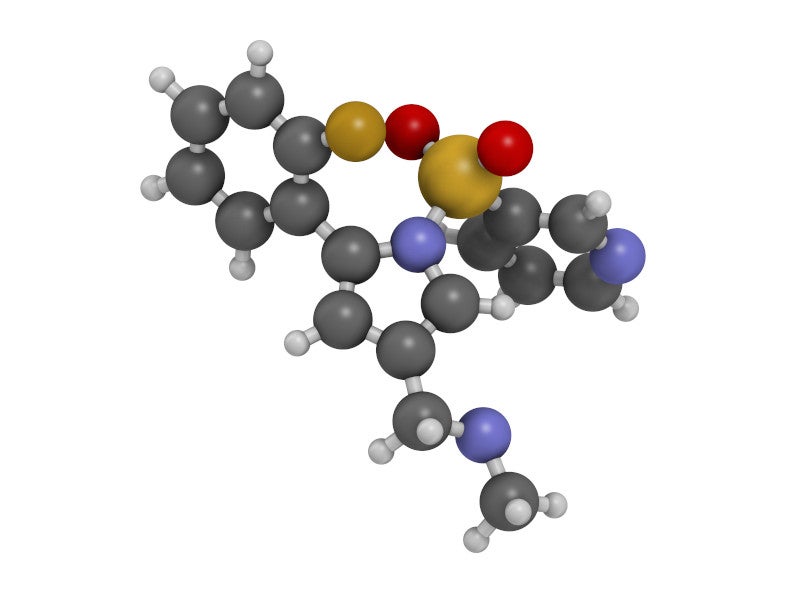
Vonoprazan is a novel, orally active, small molecule potassium competitive acid blocker (P-CAB). It is a first-in-class acid suppressant found in the VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK together with the antibiotics amoxicillin, an antibacterial drug, and clarithromycin, a macrolide antimicrobial drug, as well as in VOQUEZNA DUAL PAKs with amoxicillin only.
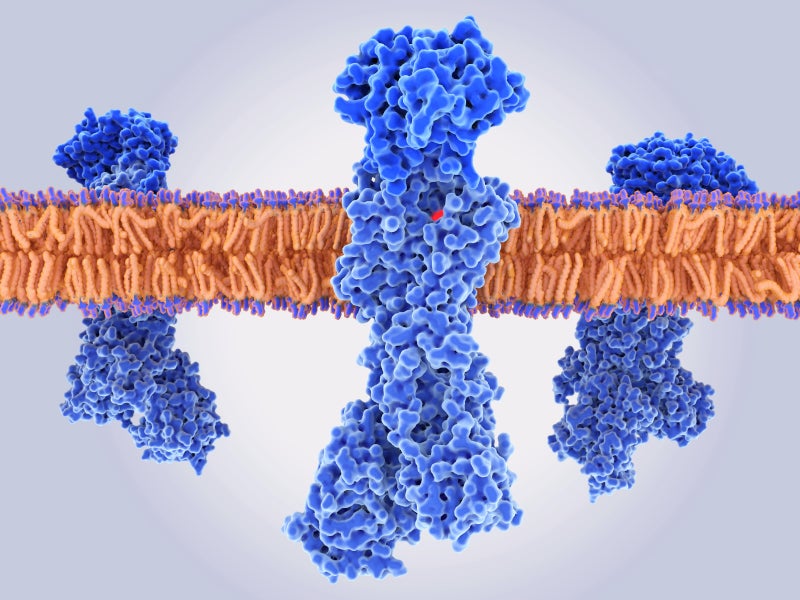
PCABs inhibit the gastric proton pump and prevent the secretion of acid in the stomach.
Vonoprazan can selectively concentrate in the acid-producing parietal cells of the stomach and suppress the acid secretion by binding to the active proton pumps in the cells in a noncovalent and reversible manner. This creates specific pH levels in the stomach that improve the effectiveness of antibiotics.
Heliobacter pylori infection symptoms and causes
Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative bacillus that causes inflammation in the acid-producing mucous layer of the stomach.
Chronic inflammation triggered by H pylori infection may lead to a range of pathologies, including dyspepsia, peptic ulcer disease, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma, chronic inflammation, and non-cardia gastric cancer. The infection can result in serious complications if left untreated.
The bacteria can spread through contaminated food, water or direct contact with saliva, vomit, or stools. H pylori infection can exhibit few or no signs or symptoms, but typical symptoms may include an ache or burning pain in the abdomen, stomach pain (worse when the stomach is empty), nausea, loss of appetite, frequent burping, bloating, and unintentional weight loss.
The acid suppressant therapy has long been recognised as a valuable method to assist H pylori treatment and improve antibiotic efficacy.
Clinical trials on VOQUEZNA
The approval of VOQUEZNA products was based on safety and efficacy data from the Phase III PHALCON-HP clinical trial, which compared VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK with lansoprazole in combination with amoxicillin and clarithromycin (lansoprazole triple therapy).
In the study, 992 patients with confirmed H pylori infection were randomised at a 1:1:1 ratio to receive either VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK or lansoprazole triple therapy for 14 days.
The study’s primary endpoint was the eradication rates of H pylori in patients. H pylori eradication was determined by a carbon-Urea Breath Test (13C-UBT), followed by upper endoscopy four weeks after the 14 days of treatment.
A negative 13C UBT test-of-cure at or more than 27 days after therapy confirms the absence of H pylori.
Both vonoprazan-based treatment regimens successfully met their primary endpoints. In the H pylori infection patient group who did not have a clarithromycin or amoxicillin resistant strain at baseline, the eradication rates were 84.7% with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and 78.5% for VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK, compared with 78.8% among patients given lansoprazole triple therapy.
Both the VOQUEZNA treatment options showed superior eradication rates compared with a standard of care proton pump inhibitor (PPI) based lansoprazole triple therapy among all groups of patients, including the patients with clarithromycin-resistant strains of H pylori. The most common adverse reactions reported with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK during the trial were diarrhoea, dysgeusia, vulvovaginal candidiasis, abdominal pain, headache, and hypertension, while diarrhoea, abdominal pain, vulvovaginal candidiasis and nasopharyngitis were the most common side effects reported in patients receiving VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK.
Phathom is also studying the use of vonoprazan for the treatment of non-erosive reflux disease (NERD).