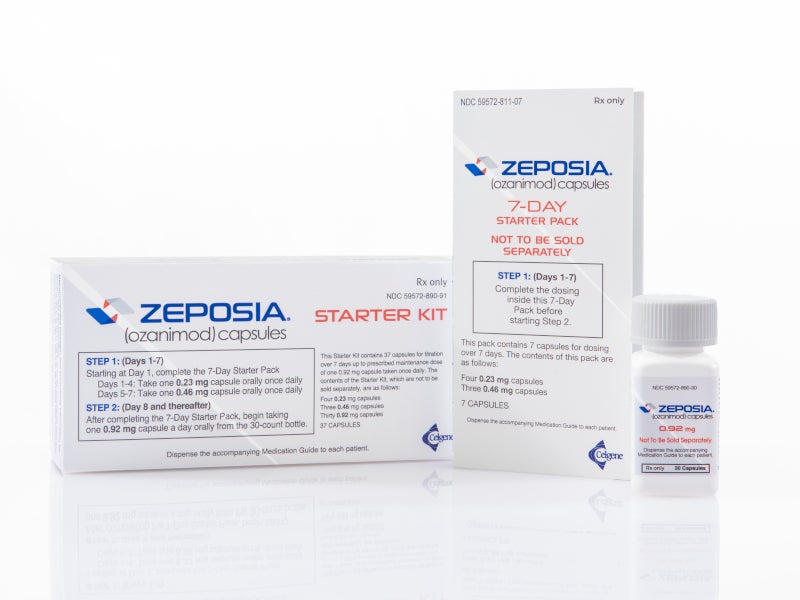
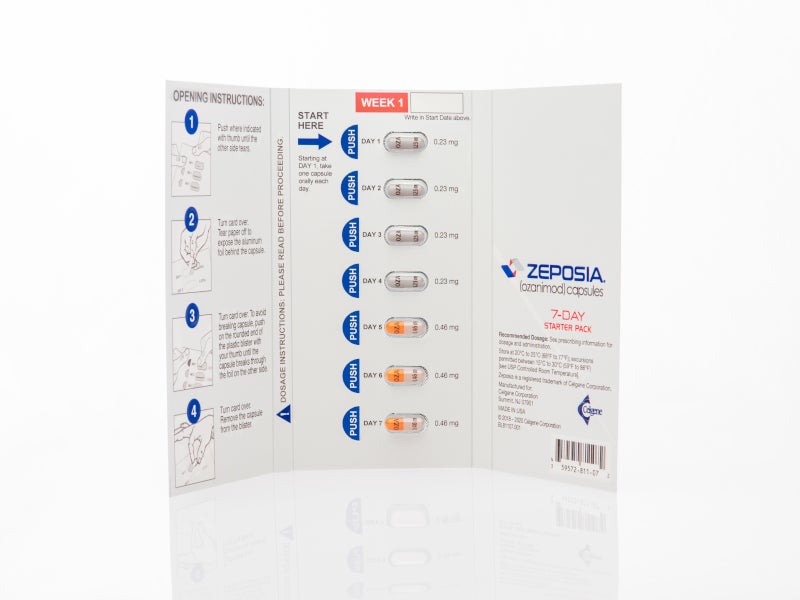
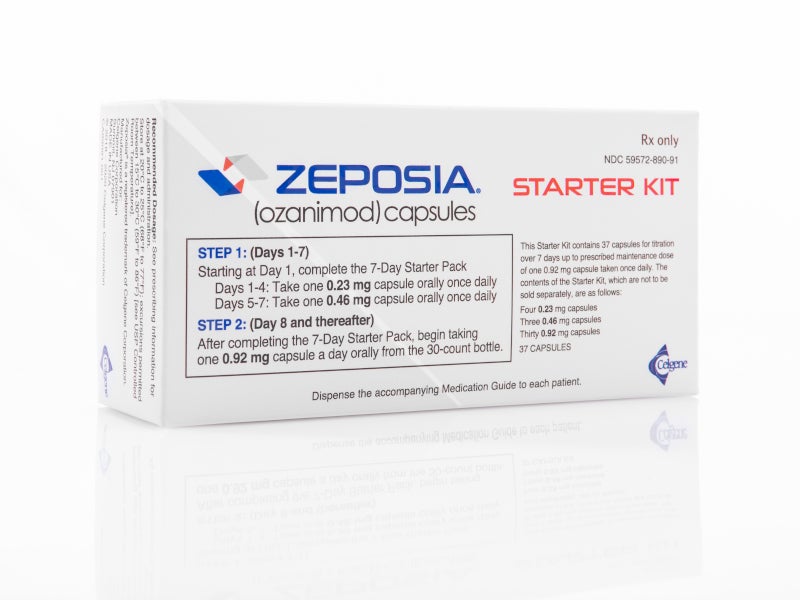
ZEPOSIA® (Ozanimod) is the only FDA approved sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulator indicated for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (RMS) in adults.
ZEPOSIA is also an effective treatment of clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive multiple sclerosis, developed by Celgene, a subsidiary of Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS). The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Ozanimod in March 2020.
The company submitted Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) for ZEPOSIA (Ozanimod) for the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in March 2019. A regulatory decision from the EMA is anticipated in the second quarter of 2020.
ZEPOSIA is available as an oral capsule with the recommended maintenance dosage of 0.92mg once daily.
Multiple sclerosis causes and symptoms
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune condition that damages the brain and spinal cord, which make up the central nervous system (CNS). It disrupts the data flow within the brain and along the nerve pathways between the brain and the body.
The exact cause of multiple sclerosis is unknown and the disease causes the immune system to attack the myelin sheath, resulting in inflammation, scars or lesions on the protective myelin layer around nerve fibres, leading to signal destruction to and from the brain.
Multiple sclerosis is one of the leading causes of non-traumatic neurological disability in young adults.
The unpredictable symptoms of multiple sclerosis are numbness, tingling, mood changes, memory problems, pain, fatigue, and blindness or paralysis. Losses can be temporary or long-lasting.
Multiple sclerosis is categorised into three types including primary progressive MS (PPMS), secondary progressive MS (SPMS) and relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS).
Ozanimod mechanism of action
Ozanimod is an oral S1P receptor modulator that targets S1P receptors 1 and 5 with high affinity.
It blocks the ability of lymphocytes to enter the CNS and reduces the number of lymphocytes in the peripheral blood.
BMS is also studying ZEPOSIA (Ozanimod) as a potential treatment for additional immune-inflammatory indications, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Clinical trials on ZEPOSIA
The safety and efficacy of ZEPOSIA were demonstrated in two randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, parallel-group, active comparator-controlled clinical trials, Phase 3 SUNBEAM and RADIANCE Part B trials.
In SUNBEAM, 1346 patients were randomised to receive 0.92mg of oral ZEPOSIA which is almost equivalent to 1mg against AVONEX® (interferon beta-1a) intramuscular injection weekly during the 12-month treatment period. In RADIANCE Part B, 1,320 patients were treated for 24 months.
The primary endpoint for SUNBEAM and RADIANCE Part B was annualised relapse rates (ARR) during the treatment periods of 12 and 24 months respectively.
The secondary MRI endpoints in SUNBEAM and RADIANCE Part B enclosed the number of new or enlarging hyper-intense T2-weighted brain MRI lesions over 24 months and the number of gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI lesions at month 24.
The most common adverse reactions observed in the patients during these trials were orthostatic hypotension, urinary tract infection, upper respiratory infection, back pain, elevation in hepatic transaminase and hypertension.
Marketing commentary on Bristol Myers Squibb
Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS) is a multinational biopharmaceutical company with a focus on developing innovative medicines for serious diseases and conditions.
Founded in 1887, BMS is based in New York, US, focusing on therapeutic areas of Cardiovascular, Oncology, Immunoscience and Fibrosis.
BMS currently has more than 50 compounds in the developmental stage and is also studying more than 40 therapy areas.